In this article, you will learn what happens to the brain during meditation and how the daily life of practitioners changes. We will not emphasize any particular type of meditation, although mindfulness meditation is the most studied in the scientific world. All types of meditation are, in fact, variants of the common and offer to work at different levels of consciousness. The challenge for the individual is, regardless of practice, to find a way to one’s self and to free oneself from stress, fears, and worries. To find support in oneself and not to be dependent on external objects that may change over time.
By the 1970s, the wave of popularity of meditative practices has already seized Europe and America, and it became clear that meditation is not a passing fad, but a serious occupation, which for a long time entered people’s lives. Scientists became interested in this phenomenon and began to study the behavioral and neurophysiological effects of meditation, its effect on improving mood, reducing stress and impact on various cognitive functions.
In the last decade, it has become known that meditation results in long-term structural changes in the brain. One experiment showed proven improvements in subjects in just eight weeks related to memory, perception, empathy, and stress.
The result of another study showed that meditators recorded an increase in gray matter volume, this was linked to emotion regulation and increased self-control. Loss of brain gray matter and cellular connections is an indicator of aging. Only 10% of the elderly are genetically protected against memory impairment and loss of brain cells, the remaining 90% inevitably lose their memory. Perhaps there is now hope for maintaining cognitive function in old age?
Meditation Conditioning
To understand the effects of meditation on a person, you need to know how it works and what the parts of the brain are responsible for.
The amygdala is a small amygdala part of the brain that activates the alert system in the presence of stimuli and stressors. The amygdala is connected to the prefrontal cortex, which helps control the brain’s chain reaction of signals.
The prefrontal cortex regulates the stress response, which began in the amygdala. When signals received by the amygdala body are perceived as a threat, the prefrontal cortex helps to assess the situation rationally, without emotion, and keep you calm. The connection between the amygdala and prefrontal cortex doesn’t develop until late adolescence, so it’s harder for a child or teenager to calm down during times of stress. Meditation improves the ability to slow down reactions and process more information.
The cerebral cortex is responsible for more complex thought processes, such as introspection and abstract thinking. Experienced meditation practitioners experience stress much more easily. If it occurs at all, because calm and sober assessment of the situation eliminates the very cause of anxiety.
The hippocampus is the memory center that affects cognitive abilities. Studies have shown that the size of this area in meditators increases by 15%.
The temporoparietal node is associated with perspective taking, empathy and compassion.
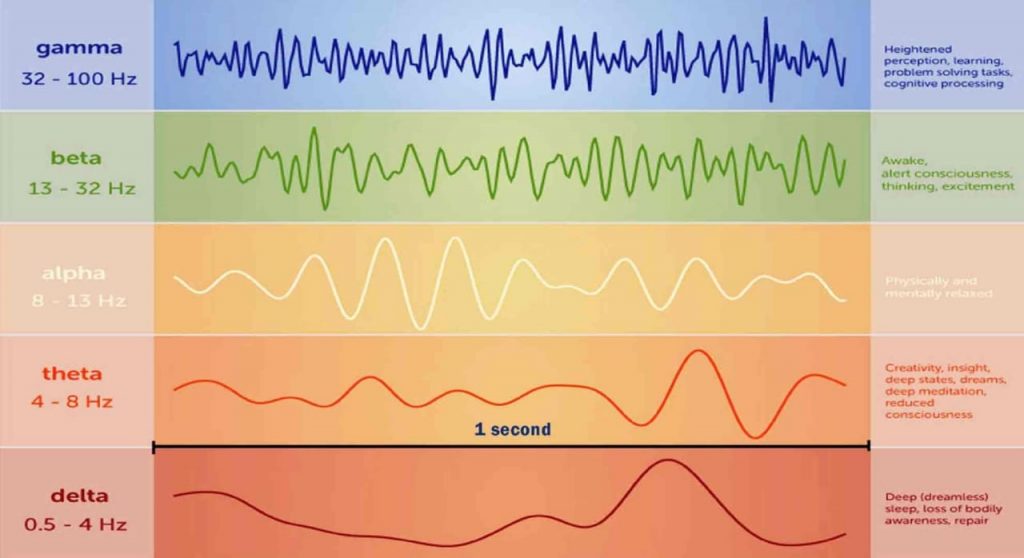
Whether we are busy doing something, resting or sleeping, the brain always has activity that can be recorded as frequencies or waves: gamma, beta, alpha, theta, delta.
Gamma waves are the fastest. They are associated with increased mental activity involving perception, learning, awareness, and problem solving.
Beta waves are present during concentration, conversation, or focused work. The electroencephalogram showed a small amount of beta waves during meditation.
Alpha waves are active in a calm, relaxed, yet alert state of mind: creative activity, the state before falling asleep, and during meditation. The normal state of the brain in the calm state is supposed to be a silent stream of thoughts, images, and memories that spontaneously appear and are not amplified by deliberate reasoning or stimulation of sensory systems. This kind of spontaneously wandering mind is one of the states of the brain during meditation that is often underestimated. It is essentially a “mental processing” of residual experiences and emotions. Immersing oneself in alpha oscillations through meditation can nurture creativity. It is the beginning of access to a calmer and more creative life experience.
Theta waves are measured during deep meditation, daydreaming or REM sleep. They can also be detected during automatic repetitive tasks that turn off the brain, such as doing the dishes. During meditation, theta waves are more active in the frontal and middle parts of the brain.
Delta waves occur during deep restorative sleep when body awareness is completely lost. Delta waves are not active during meditation, confirming the difference between meditation and sleep.
Changing Responses to Stress
Stress is the body’s natural defense against danger caused by an event or thought; it manifests as frustration, aggression, nervousness. When a stressful event occurs, the body fills up with hormones to avoid or resist danger. This is called the “fight or flight” response.
Chronic stress causes chemical changes in the body that raise blood pressure, heart rate and blood sugar levels.
Prolonged stress or high levels of stress can lead to mental health problems.
Ignoring, denying stress or distracting yourself for short periods of time has short-lived effects, but can undermine your health in the long run. Research on stress suggests that being aware of the present moment, a key feature of mindfulness, increases stress tolerance and leads to coping with stress. A person’s tendency to stay in the present moment reduces anxiety and depression and improves mood and well-being.
How does meditation reduce stress?
- You become more aware of perceived thoughts and understand where the real threat is and where it is just your projection.
- You don’t immediately react to the situation, but pause to call on your wisdom and respond appropriately.
- Meditation involves a mode of existence associated with relaxation.
- The meditation state allows you to hear your body’s needs better. Therefore, you can notice pain and other signals of unwellness earlier.
- You are more aware of the emotions of others, which happens as your emotional intelligence increases. Therefore, you are less likely to engage in conflict or find yourself in a stressful situation.
- You have an increased level of compassion for yourself and others. A compassionate mind calms and suppresses stress reactions.
- Practicing mindfulness reduces activity in the amygdala (amygdala) of the brain, which plays a key role in the emergence of the stress response. Therefore, the background level of stress is markedly reduced.
- Attitudes toward stress change. Instead of seeing only the negative effects of stress, mindfulness gives a new perspective on stress itself.
- Some studies indicate that stress is better handled by meditations in which one refrains from mind control (non-directive meditation). To get away from a stressful situation, one must allow thoughts to pass effortlessly without engaging in thought.
Improving Attention and Memory
Mindfulness is the ability to focus on the present moment and disengage from distractions or memories. This quality is often used to treat patients with depression, anxiety and other disorders. The study showed that mindfulness training increases the density of the hippocampus, which plays a key role in both working and long-term memory. In addition, the hippocampus showed plasticity after just a few hours of regular meditation.
Associated with the hippocampus is a memory property called “anticipatory interference” – difficulty remembering new material because of past and currently irrelevant information. Preemptive interference can be partially reduced by influencing the hippocampal structure during meditation.
Mindfulness regulates attention to experiencing the present moment and improves encoding of new material. Researchers have found an increase in hippocampal gray matter density in healthy individuals and adults with Parkinson’s disease, and a decrease in hippocampal atrophy in adults with mild cognitive impairment.
The link between hippocampal size and working memory in healthy adults is particularly important because working memory affects many other cognitive functions, such as problem solving efficiency, language comprehension, and reasoning ability. The quality of all of these vital brain functions can be improved in mindfulness meditation.
In addition to helping to improve critical cognitive functions, mindfulness can be a useful component of treatment for other conditions associated with memory impairment and decreased hippocampal volume, such as post-traumatic stress disorder.
Reducing Anxiety
We all experience feelings of anxiety from time to time. But there is a difference between everyday anxiety and clinical anxiety. Normal anxiety becomes a generalized anxiety disorder when the fear or worry does not subside, but escalates into panic, a sense of impending doom, or constant thoughts of disaster.
Stress can also cause anxiety, and there are similarities between the two conditions in terms of physiological responses. Stress is a heightened emotional state that goes away after the stressful situation is over, whereas anxiety tends to persist for a long time.
Diagnosable anxiety disorders:
- General anxiety.
- Social anxiety.
- Separation anxiety.
- Panic disorder.
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Through meditation, one learns to understand the deceptive nature of anxiety and to recognize provoking thoughts. From this state, you can find ways to bypass mental patterns, avoiding falling back into the trap of anxiety. Consistent meditation practice reprograms your perception of reality and improves your ability to regulate your emotions.
How does meditation work with anxiety? Through meditation, one becomes familiar with anxiety-provoking thoughts and storylines. One learns to see them, analyze them, and let them go. In doing so, you learn two important things: thoughts do not define us, and thoughts are not real. From this new perspective, you change your relationship to anxiety, distinguishing between what is an irrational reason and what is true. If you begin to engage in authentic meditations, proven over thousands of years, stability in the perception of reality is manifested and the very ground for anxiety disappears.
Changing the volume of the brain
Brain scans of meditators showed an increase in the thickness of the parts of the brain responsible for attention and sensory information processing. And the increase in gray matter was more pronounced in older practitioners than in younger people who did not meditate. Scientists were particularly interested in this fact because these areas of the cerebral cortex usually thin out with age.
Meditation causes physical changes in the brain because of neuroplasticity-the brain’s ability to constantly change. Life forces the brain to constantly make new neural connections, so neurons (nerve cells) are actively adapting to respond to changes in the environment.
The way you think and feel changes the neural structures and shape of the brain. Studies have shown that it only takes eight weeks of practice to change the shape and increase gray matter. This type of tissue is important in areas responsible for muscle control, sensory perception, emotions, memory, decision-making and self-control.
Meditation can briefly relax and calm your emotions. But it can also permanently change your brain if you approach this practice as a form of mindfulness training. Different teachers can teach all kinds of meditation, but you have to find your own on your own. Science proves that if one makes a regular effort to reprogram oneself, it will definitely work and improve not only the quality of the brain, but will also change one’s worldview. The world of thought with which meditation works, it turns out, directly affects both your daily well-being and the events of your future. As you know, what you think about today becomes your tomorrow. Hygiene of thought conditions the future of developed humanity. Please keep your thoughts clean.







